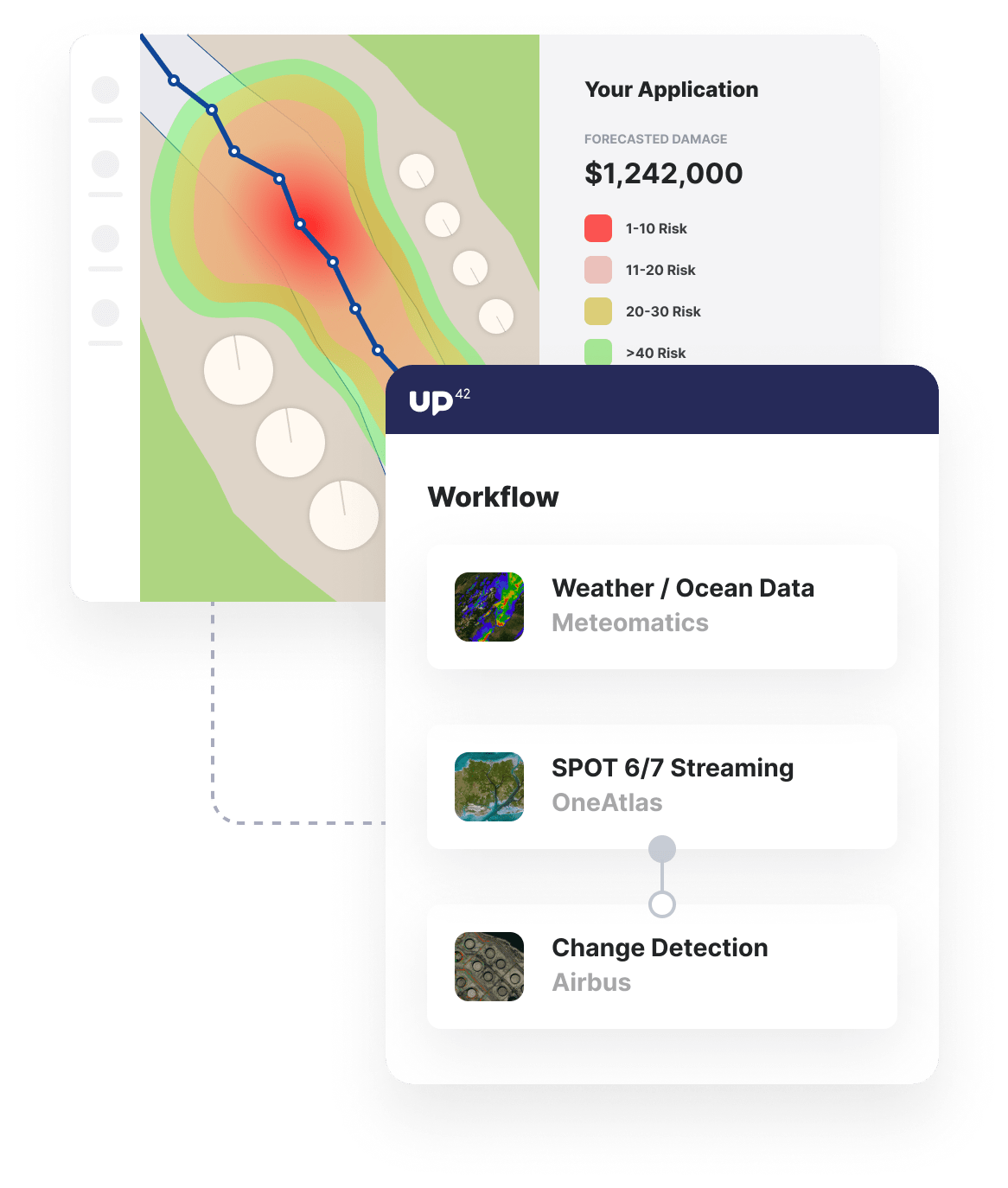
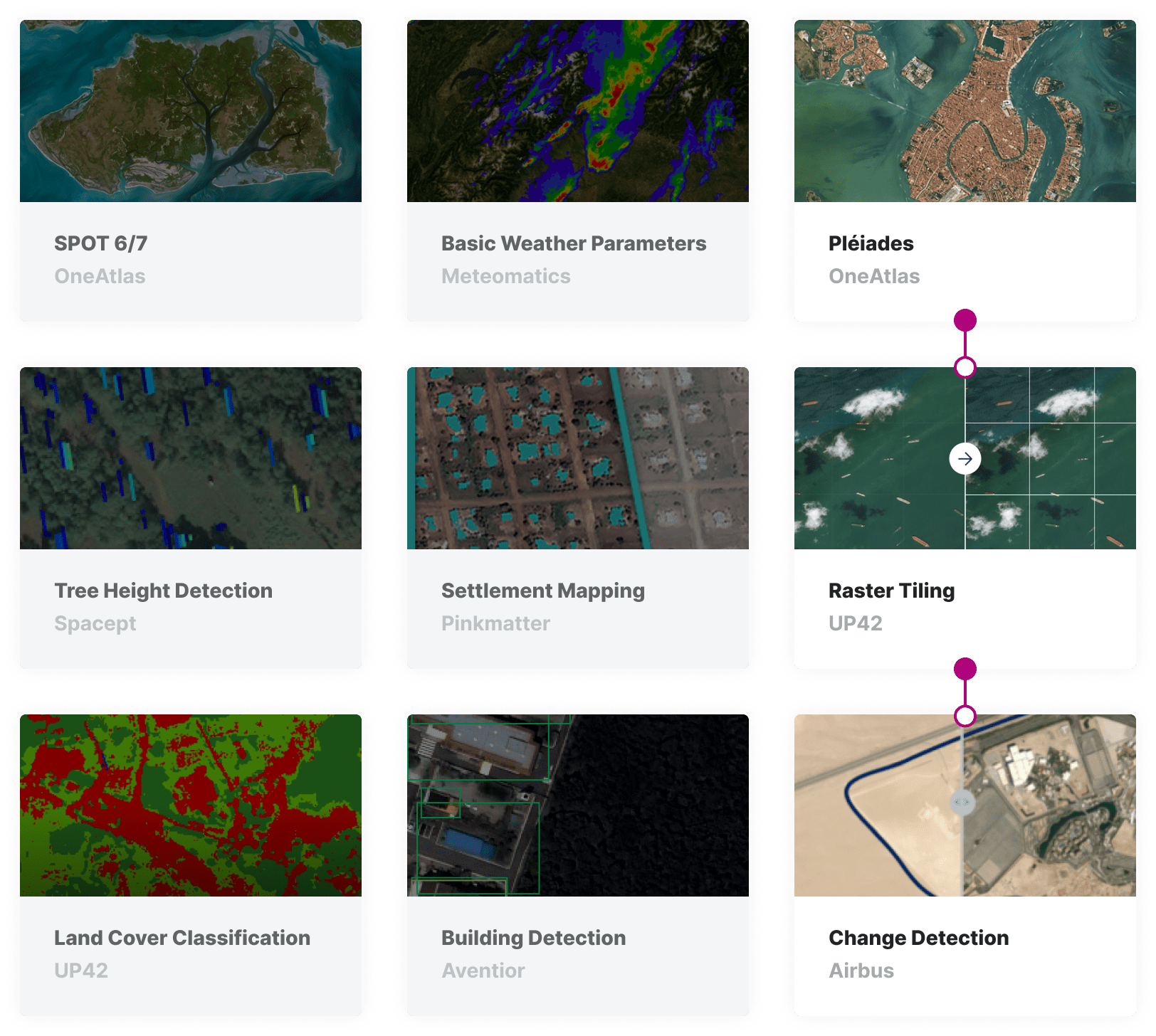
High-resolution imagery and weather data
Monitor assets using high-resolution, high-revisit-rate satellites to provide recent imagery of assets. Augment analysis with 1000 weather parameters.
Change detection and risk prediction
Detect change to areas surrounding pipeline infrastructure and implement alert systems for high-risk weather conditions.
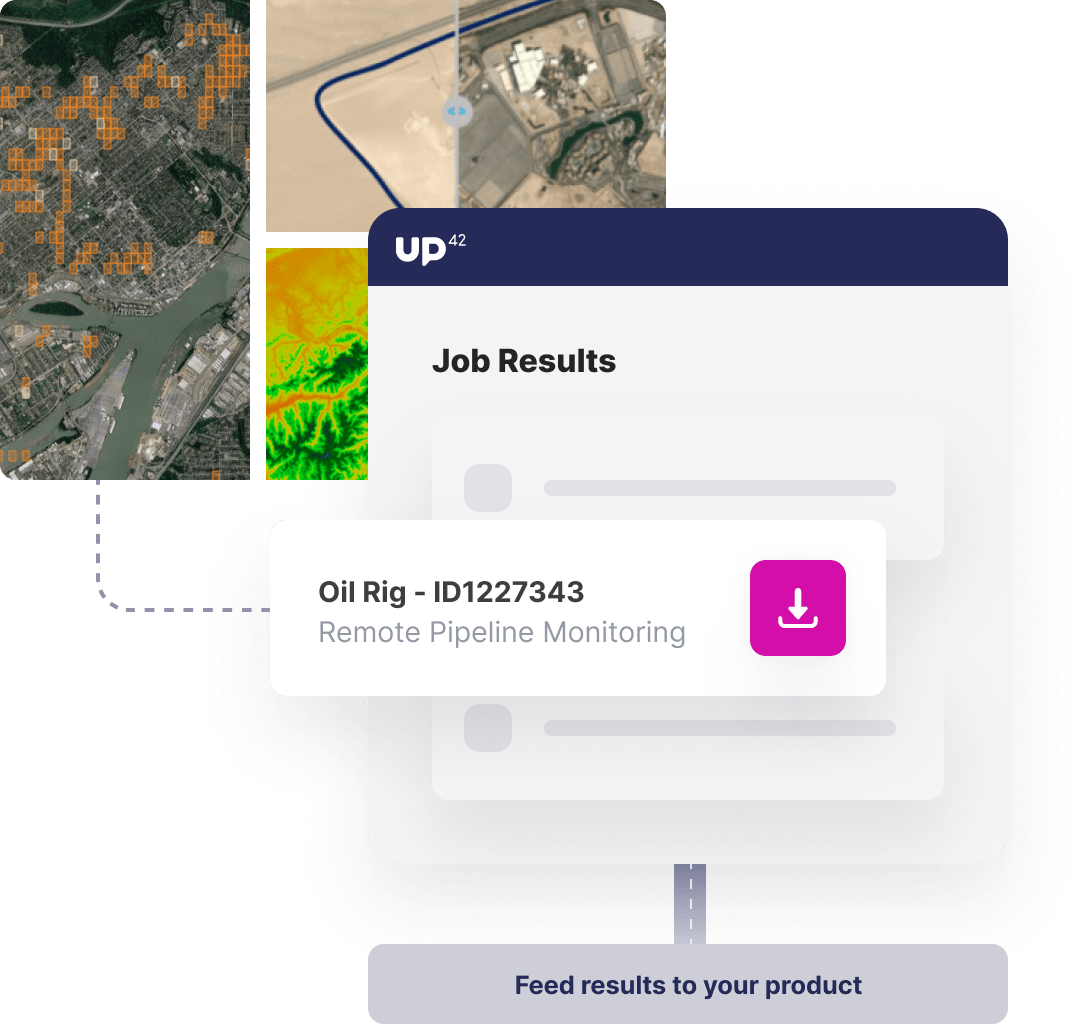
Integrate into alert systems
Use our toolkit to seamlessly integrate data and processing outputs into existing or new geospatial products and early warning systems.