If you need multiple passes to capture your area of interest (AOI), you might run into some challenges. Differences between sensors or viewpoint angles can result in misalignment. To solve this, we’ll explore how to use the coregistration algorithm from our partner Simularity to achieve maximum alignment between images and ensure more accurate analysis on the UP42 platform, resulting in a higher return on image investment and enabling new, valuable discoveries that were previously not possible with misaligned images.
What is coregistration?
The coregistration process accurately aligns different images of the same AOI. In other words, it superimposes the images to enable a more effective combination or comparison of the information they contain. They may come from the same or different sensors. Coregistration is essential across various industries and applications where multiple images need to be compared to each other, including mapping, disaster management, and monitoring environmental and land changes such as vegetation health, deforestation, or urban growth.

There are many benefits to performing coregistration:
- Improved accuracy: By ensuring that images from different times, sensors, or angles are aligned and correspond to the same location, coregistration reduces false interpretation. For example, in a recent customer pilot project we measured positional accuracy improvements, achieving a 2X median enhancement—from 4.2 m to 2.11 m—by aligning Pléiades NEO imagery to a high-accuracy DOP20 reference.
- Prerequisite for precise change detection: Coregistration enables an easier comparison of images that are taken at different times. This is especially useful as change detection algorithms can be quite “noisy”, detecting all changes. Coregistration enables you to ignore any noise arising from misaligned images (pixel displacements) and focus on the real-world changes you want to find.
- Improved fusion of multi-source images: It allows for the seamless integration of multitemporal and multispectral datasets. Different types of data help to create a more comprehensive view of a given AOI, and improve the reliability of the final output.
- Increased findings: With more possible combinations of input images and improved alignment accuracy, previously overlooked scenarios—once hidden in plain sight—can now be detected.
- Enhanced DEM generation: Coregistration reduces geometric distortions and ensures a better alignment of stereo data, or data from different sensors.
Coregistration from our partner Simularity
UP42’s platform hosts several enhancement algorithms that allow you to transform geospatial assets into analysis-ready data. One such algorithm is Simularity’s Image Coregistration (COREG). It aligns an image to the reference image by performing automatic detection and correction of sub-pixel misalignments between different datasets. It is independent of spatial or spectral characteristics and robust against high degrees of cloud coverage, or spectral and temporal land cover dynamics.
The algorithm uses the Rigid-Body coregistration: the image pixels are not changed relative to each other, but the image itself is moved to the position that best matches the reference image. This helps to preserve the image integrity and the relationship between pixels, while at the same time providing the most optimal coregistration. The algorithm uses one reference image (which remains unchanged) and one source image that is coregistered in a way so that its pixels are aligned to minimize registration error for the entire end output.
The algorithm can be used with all collections that produce multispectral or panchromatic bands, but the image should be at the same processing level for the most effective coregistration. In addition, orthorectification improves the coregistration results in cases of significant elevation changes, but it’s not a prerequisite to run the algorithm. Any resolution is acceptable, as long as the reference and source images are similar. Lastly, quality will naturally increase with smaller viewing angles, but there are no restrictions here.
The coregistration process significantly improves alignment accuracy; however, its effectiveness can be slightly influenced by factors such as the quality of the initial alignment and the presence of distinct features in the imagery. Optimal results are achieved when working with smaller initial offsets and areas rich in reliable control points.
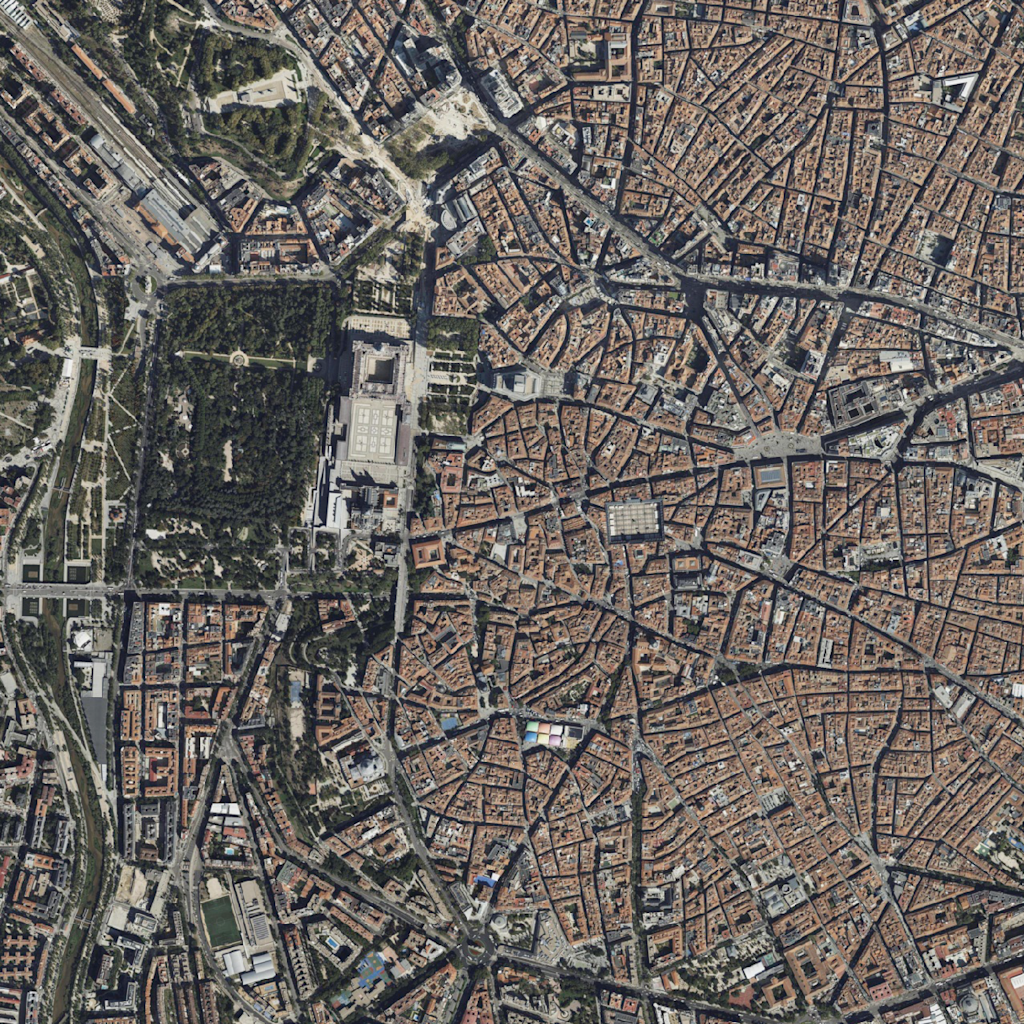
 Coregistration, original image
Coregistration, original image
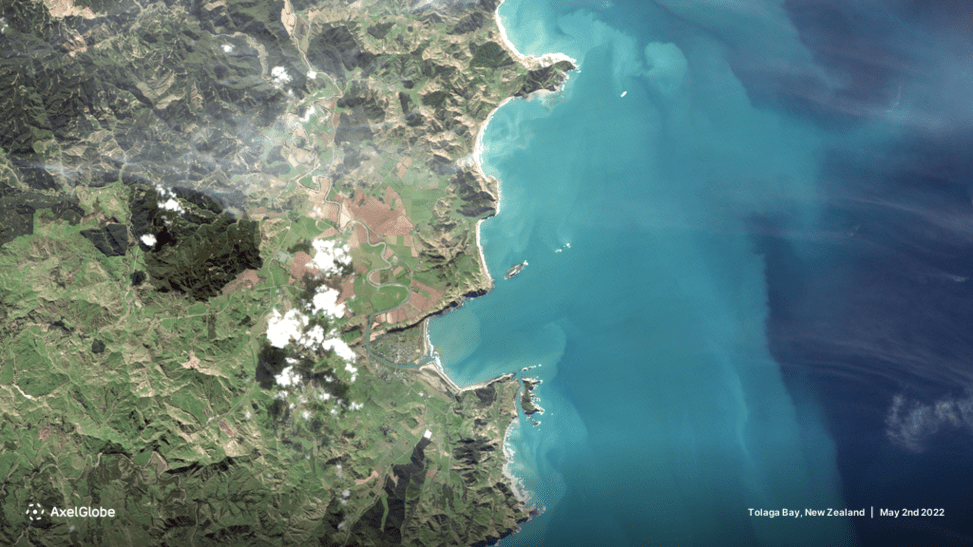
 Coregistration, shifted image
Coregistration, shifted image
Why use coregistration on the UP42 platform?
UP42 leverages STAC to ensure cross-sensor metadata harmonization and standardizes all deliveries into cloud-native formats (e.g., COGs). And if this isn’t enough to give it a try, let’s look at some additional benefits:
- Precise results: State-of-the-art coregistration algorithm to give the most accurate results. Focus on your core business and let UP42 do all the heavy lifting with data pre-processing.
- Ease of use: Order data, run one or multiple processes, see results in data management, or download and view in QGIS or your GIS of choice using streaming links to COGs, API, or SDK.
- Scalability: run on UP42 infrastructure (no need to set up and maintain your own), you can coregister dozens of images at the same time.
Running coregistration on the platform is easy. But don’t take our word for it—try it out today or reach out to our customer success team if you have any questions or simply need help to get started.